Orchestrating RPA Bots
After setting up all components in the Installation & Configuration, we will now dive into a concrete example of setting up RPA Orchestration. If your example is already up and running and you would like to dig deeper into Error Handling, go ahead.
Creating and deploying a Bot
UiPath
To orchestrate your RPA bots and the tasks that they automate, you need to create a UiPath package that contains the scripts that the RPA bots should execute. In UiPath, these scripts are called “Process”.
The data that these scripts need as input should be configured as IN arguments in UiPath Studio. The RPA Bridge will then pass the Camunda task input parameters via the UiPath Orchestrator into the UiPath Robot. In a similar way, the OUT arguments of UiPath will be returned back into the Camunda engine as task output parameters. The names of these IN and OUT arguments will be used in the Cawemo Catalog.
Once the UiPath script works as expected, it needs to be deployed into the UiPath Orchestrator as a new package. The name of this package will be used in the Cawemo Catalog.
Please make sure that the UiPath Orchestrator can successfully trigger a UiPath Robot to execute the given package.
In case you have trouble setting up and running your UiPath scripts via the UiPath Orchestrator, please refer to the UiPath documentation.
Automation Anywhere
Orchestrating an RPA bot in AutomationAnywhere can be done via Automation Anywhere Control Room. When creating a new bot Automation Anywhere will ask for a name for the new bot. This name will be used to reference the bot from the Cawemo Catalog and eventually from the BPMN model. Make sure it is unique in your Automation Anywhere installation to avoid unwanted behavior.
If the new bot uses input and/or output variables, make sure to configure those variables correctly as input or output variables in the bot editor in Automation Anywhere Control Room. To provide input variables to the bot, configure input mapping for each variable that should be passed to the bot on the task through either Cawemo or the Camunda Modeler. To send output variables from the bot to Camunda, configure input mapping on the task through either Cawemo or the Camunda Modeler and make sure to mark the variables as output in the Automation Anywhere Control Room.
Once the RPA bot works as expected and is released, make sure that the bot and all necessary resources are available publicly.
In case you have trouble setting up and running your Automation Anywhere scripts via the Automation Anywhere Control Room, please refer to the Automation Anywhere documentation.
Adding a template to the Catalog
For each UiPath package that should be orchestrated, there needs to be a corresponding template in the Cawemo Catalog.
To create a new template, you need to:
- Open the “Home” view of Cawemo
- Create a new “Catalog Project” using the split button and give it a name
- Create a new “Service Task Template” inside this new catalog project
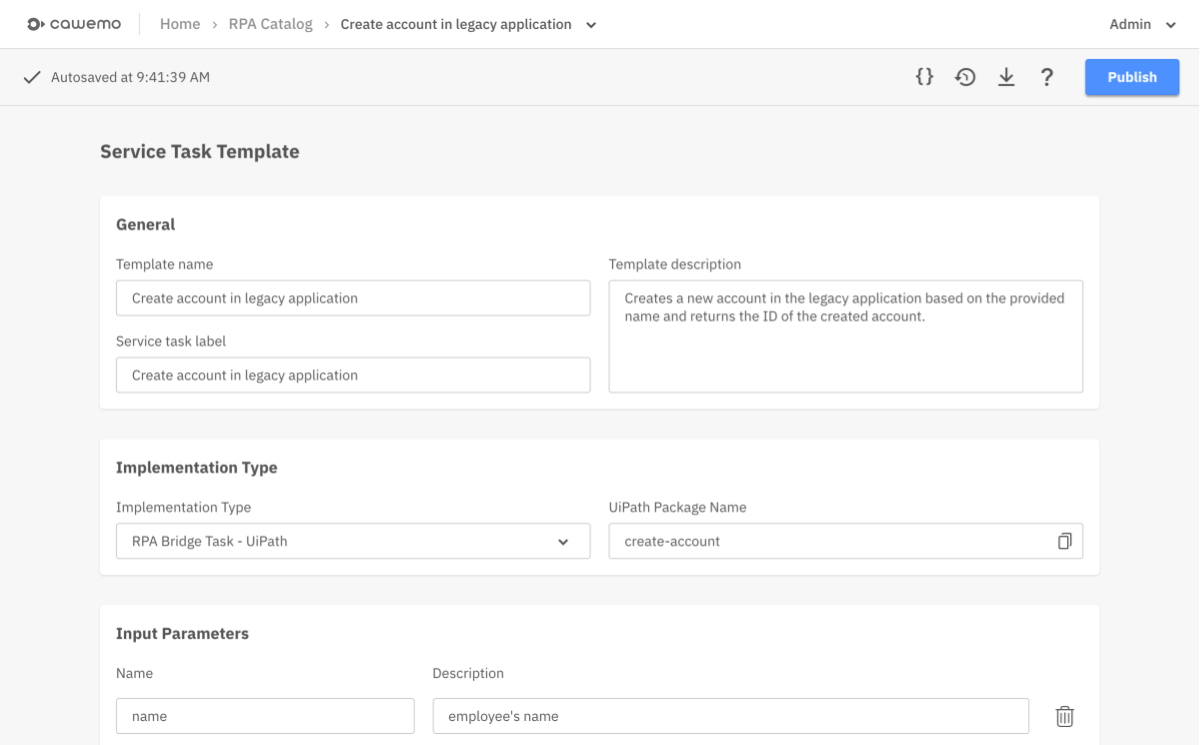
Edit the template as follows:
- General
- Template name: Define a human-readable name, such that users will understand which RPA bot this template refers to
- Service task label: Leave empty if you do not want to give a default label to the BPMN service task
- Implementation Type
- Implementation Type: Choose either UiPath or Automation Anywhere
- UiPath Package Name: Add the package name that you defined in UiPath Orchestrator
- Automation Anywhere Bot Name: Add the bot name you defined in Automation Anywhere
- Input Parameters
- For each RPA bot input argument, add one entry with the matching name
- Output Parameters
- For each RPA bot output argument, add one entry with the matching name
Descriptions: In order to provide details on how to use the template, explain what the RPA bot does or what values each parameter expects. The descriptions will be shown in the Camunda Modeler when the template is being used.
Before a template can be used in the Camunda Modeler, it needs to be published once by clicking the “Publish” button in the upper right corner. If you like, you can provide a name for the published version. If you need to adjust your template later on, you can publish a new version of it.
If you want to create templates for other elements, you can learn more about advanced configuration options.
Modeling and executing a process
The Camunda Modeler updates the list of available templates when being launched. In order to enforce a synchronization of the templates, click on the Cawemo logo in the upper right corner and save the configuration dialog again. You will see a notification about the templates that have been synched.
To trigger the RPA Bot from Camunda, create a new BPMN process as follows:
- Create new BPMN process diagram
- Append a new Task to the Start Event and turn it into a Service Task (remember to use the Wrench icon next to the task for changing its type)
Use templates
- Click on “Catalog” in the Property Panel, and you will see an overlay with a list of your templates
- Select one template and click Apply. With the template being applied, you see a simplified Property Panel
- For any Input Parameter:
- Define the value that should be passed to the RPA Bot
- Variable Assignment Value can be a String constant or a process variable that is passed via an Expression
- For any Output Parameter:
- Define the name of a process variable that this output value should be assigned to
Enhance your process diagram:
- Complete your BPMN process diagram with further elements as you see fit (e.g., User Tasks)
- Finish the diagram with an End Event
Execute the process:
- Click the Run icon in the toolbar (“Start Current Diagram”) and confirm the dialogs. This will deploy the process diagram and trigger a new process instance.
- In the success notification, click on “Open in Camunda Cockpit”. You will see the running process instance with its current state.
UiPath
With the process instance running, you may observe a new Job in UiPath Orchestrator that was added by the RPA Bridge and the UiPath Robot executing the previously defined package.
Shortly after the Job is completed in UiPath, you can switch back to the Camunda Cockpit and observe the progress of your process instance. Remember that you might need to switch to the History View in case your process ends after the RPA task.
In case of an error with the UiPath Robot, you will see a new incident for the process instance in Camunda Cockpit. Depending on the specific error, you may retry to execute the Service Task and trigger UiPath again to resolve the incident.
Automation Anywhere
After starting a new process instance and reaching the RPA Service Task, you can see new entries in the historical activity lists in the Automation Anywhere Control Room representing the started RPA bot.
When the bot has completed, you can switch back to the Camunda Cockpit and observe the progress of your process instance. Remember that you might need to switch to the History View in case your process ends after the RPA task.
In case of an error with the Automation Anywhere Robot, you will see a new incident for the process instance in Camunda Cockpit. Depending on the specific error, you may retry to execute the Service Task and trigger Automation Anywhere again to resolve the incident.