Invoke an EJB from a BPMN 2.0 Service Task
In this section we learn how to call an EJB from a BPMN 2.0 Service Task.
Add EJB Service Task
After the process has been started with the new order as process variables, we want to persist the order to the database and only save the newly generated order id as process variable.
Add an Entity Bean to the Process Application
To persist the entity with JPA, we add an entity bean to our process application. Create a package org.camunda.bpm.getstarted.pizza and then place the following OrderEntity class into that package:
Camunda dropped support for handling JPA entities as variables.
Camunda Automation Platform 7.19 is the last release that supports handling JPA entities as variables
You need to add a process engine plugin to achieve some of the next steps in the guide. Have a look at the 7.20 update guide for more information.
package org.camunda.bpm.getstarted.pizza;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Version;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
public class OrderEntity implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue
protected Long id;
@Version
protected long version;
protected String customer;
protected String address;
protected String pizza;
protected boolean approved;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public long getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(long version) {
this.version = version;
}
public String getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(String customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPizza() {
return pizza;
}
public void setPizza(String pizza) {
this.pizza = pizza;
}
public boolean isApproved() {
return approved;
}
public void setApproved(boolean approved) {
this.approved = approved;
}
}
The entity class has to be annotated with @Entity and needs an @Id field. We also add a @Version field to the entity bean. This enables optimistic locking and ensures integrity during merges.
Add an EJB to the Process Application
The next step is to add a stateless EJB to the process application which is called by the process. In this EJB we inject the entity manager. It is used to manage our persistent objects during the session.
In the method persistOrder, a new instance of the order entity is created and the order instance will be initialized with the values which are currently saved as process variables. After the newly created instance is flushed to the database, its order id is set and the other process variables are no longer needed, so we remove the order properties and only add the order id as a process variable.
package org.camunda.bpm.getstarted.pizza;
import org.camunda.bpm.engine.delegate.DelegateExecution;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.inject.Named;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import java.util.Map;
@Stateless
@Named
public class OrderBusinessLogic {
// Inject the entity manager
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void persistOrder(DelegateExecution delegateExecution) {
// Create new order instance
OrderEntity orderEntity = new OrderEntity();
// Get all process variables
Map<String, Object> variables = delegateExecution.getVariables();
// Set order attributes
orderEntity.setCustomer((String) variables.get("customer"));
orderEntity.setAddress((String) variables.get("address"));
orderEntity.setPizza((String) variables.get("pizza"));
/*
Persist order instance and flush. After the flush the
id of the order instance is set.
*/
entityManager.persist(orderEntity);
entityManager.flush();
// Remove no longer needed process variables
delegateExecution.removeVariables(variables.keySet());
// Add newly created order id as process variable
delegateExecution.setVariable("orderId", orderEntity.getId());
}
}
Configure the EJB in the Process
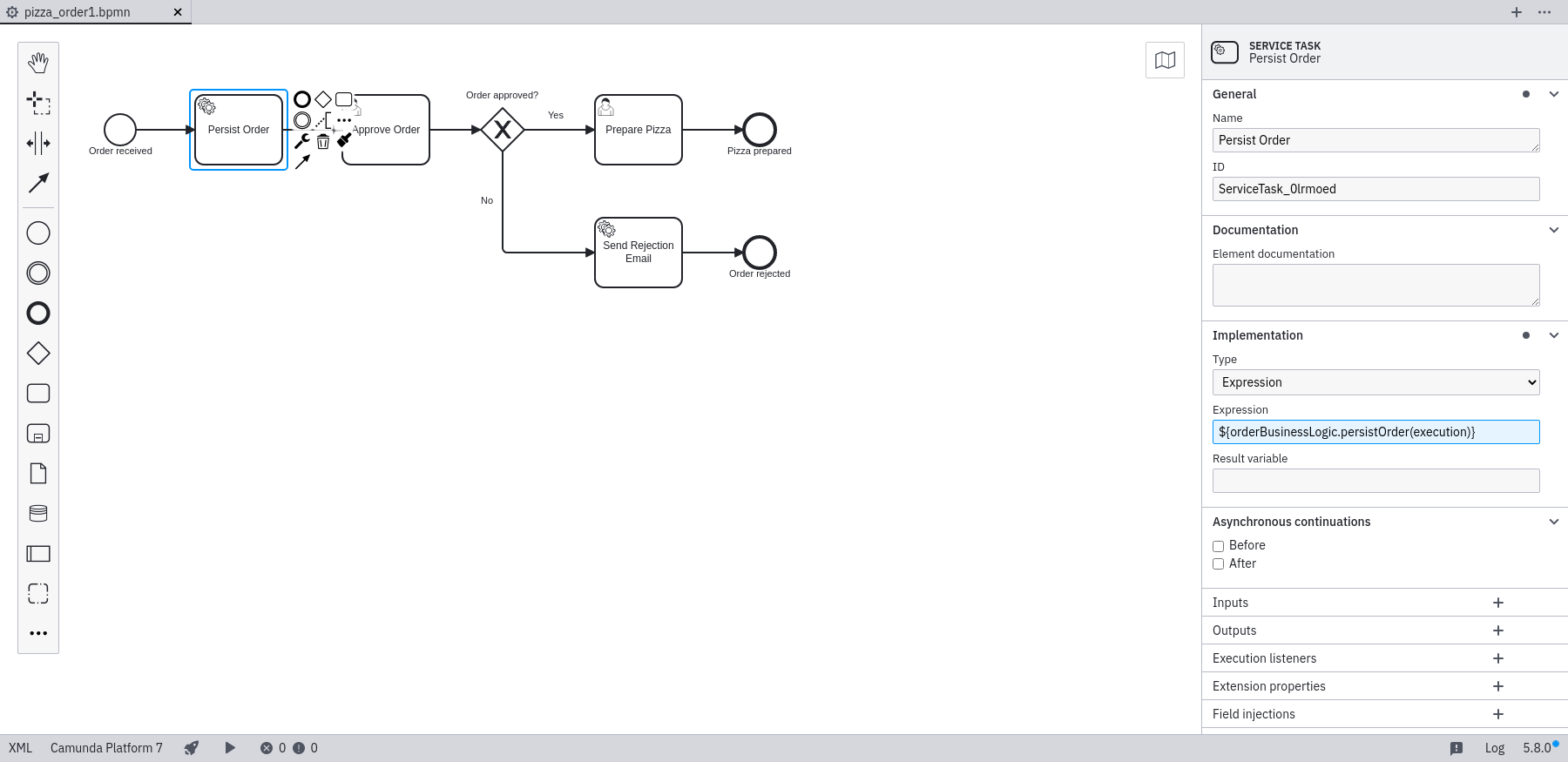
Use the properties view of the Persist Service Task in the process (see screenshot). You need to enter ${orderBusinessLogic.persistOrder(execution)} as the Expression property. This will call the persistOrder method of the named EJB with the current execution as parameter.
Build, deploy and start the process Order Pizza in Tasklist. Fill out the emerging form. Now the Persist Order step should have been completed automatically. Check that by looking into the logfile of the WildFly server. It will show an entry for the new order entity:
INFO [stdout] Hibernate: insert into OrderEntity (address, approved, customer, pizza, version, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
Catch up: Get the Sources of Step-5.
Download as .zip or checkout the corresponding tag with Git.
You can checkout the current state from the GitHub repository.
If you have not cloned the repository yet, please execute the following command:
git clone https://github.com/camunda/camunda-get-started-javaee.git
To checkout the current state of the process application please execute the following command:
git checkout -f Step-5Or download as archive from here.