Create a Model
To create a new BPMN model from scratch you have to create an empty BPMN model instance with the following method:
BpmnModelInstance modelInstance = Bpmn.createEmptyModel();
The next step is to create a BPMN definitions element. Set the target namespace on it and add it to the newly created empty model instance.
Definitions definitions = modelInstance.newInstance(Definitions.class);
definitions.setTargetNamespace("http://camunda.org/examples");
modelInstance.setDefinitions(definitions);
Usually you want to add a process to your model. This follows the same 3 steps as the creation of the BPMN definitions element:
- Create a new instance of the BPMN element
- Set attributes and child elements of the element instance
- Add the newly created element instance to the corresponding parent element
Process process = modelInstance.newInstance(Process.class);
process.setId("process");
definitions.addChildElement(process);
To simplify this repeating procedure, you can use a helper method like this one.
protected <T extends BpmnModelElementInstance> T createElement(BpmnModelElementInstance parentElement, String id, Class<T> elementClass) {
T element = parentElement.getModelInstance().newInstance(elementClass);
element.setAttributeValue("id", id, true);
parentElement.addChildElement(element);
return element;
}
After you created the elements of your process like start event, tasks, gateways and end event, you have to connect the elements with sequence flows. Again, this follows the same 3 steps of element creation and can be simplified by the following helper method.
public SequenceFlow createSequenceFlow(Process process, FlowNode from, FlowNode to) {
String identifier = from.getId() + "-" + to.getId();
SequenceFlow sequenceFlow = createElement(process, identifier, SequenceFlow.class);
process.addChildElement(sequenceFlow);
sequenceFlow.setSource(from);
from.getOutgoing().add(sequenceFlow);
sequenceFlow.setTarget(to);
to.getIncoming().add(sequenceFlow);
return sequenceFlow;
}
Validate the model against the BPMN 2.0 specification and convert it to an XML string or save it to a file or stream.
// validate the model
Bpmn.validateModel(modelInstance);
// convert to string
String xmlString = Bpmn.convertToString(modelInstance);
// write to output stream
OutputStream outputStream = new OutputStream(...);
Bpmn.writeModelToStream(outputStream, modelInstance);
// write to file
File file = new File(...);
Bpmn.writeModelToFile(file, modelInstance);
Example 1: Create a Simple Process With One User Task
With the basic helper methods from above it is very easy and straightforward to create simple processes. First, create a process with a start event, user task and an end event.
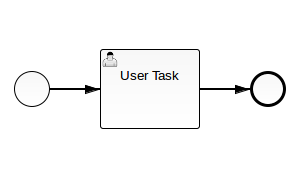
The following code creates this process using the helper methods from above (without the DI elements).
// create an empty model
BpmnModelInstance modelInstance = Bpmn.createEmptyModel();
Definitions definitions = modelInstance.newInstance(Definitions.class);
definitions.setTargetNamespace("http://camunda.org/examples");
modelInstance.setDefinitions(definitions);
// create the process
Process process = createElement(definitions, "process-with-one-task", Process.class);
// create start event, user task and end event
StartEvent startEvent = createElement(process, "start", StartEvent.class);
UserTask task1 = createElement(process, "task1", UserTask.class);
task1.setName("User Task");
EndEvent endEvent = createElement(process, "end", EndEvent.class);
// create the connections between the elements
createSequenceFlow(process, startEvent, task1);
createSequenceFlow(process, task1, endEvent);
// validate and write model to file
Bpmn.validateModel(modelInstance);
File file = File.createTempFile("bpmn-model-api-", ".bpmn");
Bpmn.writeModelToFile(file, modelInstance);
Example 2: Create a Simple Process With Two Parallel Tasks
Even more complex processes can be created with a few lines of code with the standard BPMN model API.
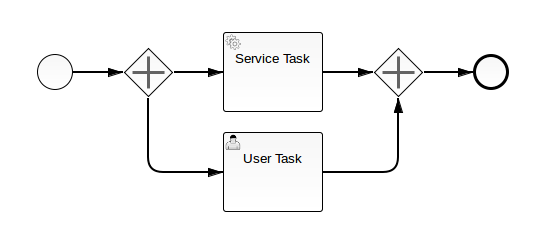
// create an empty model
BpmnModelInstance modelInstance = Bpmn.createEmptyModel();
Definitions definitions = modelInstance.newInstance(Definitions.class);
definitions.setTargetNamespace("http://camunda.org/examples");
modelInstance.setDefinitions(definitions);
// create elements
StartEvent startEvent = createElement(process, "start", StartEvent.class);
ParallelGateway fork = createElement(process, "fork", ParallelGateway.class);
ServiceTask task1 = createElement(process, "task1", ServiceTask.class);
task1.setName("Service Task");
UserTask task2 = createElement(process, "task2", UserTask.class);
task2.setName("User Task");
ParallelGateway join = createElement(process, "join", ParallelGateway.class);
EndEvent endEvent = createElement(process, "end", EndEvent.class);
// create flows
createSequenceFlow(process, startEvent, fork);
createSequenceFlow(process, fork, task1);
createSequenceFlow(process, fork, task2);
createSequenceFlow(process, task1, join);
createSequenceFlow(process, task2, join);
createSequenceFlow(process, join, endEvent);
// validate and write model to file
Bpmn.validateModel(modelInstance);
File file = File.createTempFile("bpmn-model-api-", ".bpmn");
Bpmn.writeModelToFile(file, modelInstance);