Install the Full Distribution on an IBM WebSphere Server
This section will describe how you can install the Camunda Platform and its components on an IBM WebSphere.
Reading this Guide
Throughout this guide we will use a number of variables to denote common path names and constants. You don’t have to create these variables in your environment. They are just used in this guide to make it more readable.
$WAS_HOME: points to the IBM WebSphere application server main directory (typically something like/opt/IBM/WebSphere/AppServer).$PLATFORM_VERSIONdenotes the version of the Camunda Platform you want to install or already have installed, e.g.,7.15.6-ee.$WAS_DISTRIBUTIONrepresents the downloaded Camunda Platform distribution for the IBM WebSphere Application Server, e.g.,camunda-ee-ibm-was-$PLATFORM_VERSION.zip.
The distribution is available at the Camunda enterprise release page. You will be asked to enter the credentials you received during the trial or subscription process.
Setup
Before you can install the Camunda components, you need to perform a number of required setup steps.
Resource Configuration
The Camunda Platform requires a set of resources that need to be configured at the application server level:
- One or multiple datasources to be used by the engine(s).
- A work manager for the job executor.
Define Resources in the right Scope
In order to perform the steps listed in this guide, make sure you understand the concept of management scopes introduced by the IBM WebSphere Application Server. We assume that resources are defined at the “Node” scope.
Create the Database Schema and Tables
In the default configuration of the distribution, the database schema and all required tables are automatically created in an H2 database when the engine starts up for the first time. If you do not want to use the H2 database, you have to
- Create a database schema for the Camunda Platform yourself.
- Install the database schema to create all required tables and default indices using our database schema installation guide.
When you create the tables manually, then you have to configure the engine to not create tables at startup by setting the databaseSchemaUpdate property to false (or, in case you are using Oracle, to noop). In WebSphere, this is done in the bpm-platform.xml, located in the $WAS_HOME\modules\camunda-ibm-websphere-ear-$VERSION.ear\camunda-ibm-websphere-service.jar\META-INF\ folder.
JDBC/Datasource Configuration
Camunda Platform uses one or multiple process engines which must be connected to a datasource. Use your application server management tooling for the configuration of the datasources. The JNDI name of the datasource must be equal to the name used in the datasource-Element of the process engine(s) configured in the bpm-platform.xml file.
Related resources:
- WebSphere 8.5: Configuring a JDBC provider and data source
- Websphere 9.0: Configuring a JDBC provider and data source
Default JNDI Name
The default JNDI name used by the process engine is jdbc/ProcessEngine
The following screenshot shows the configuration of an XA datasource:
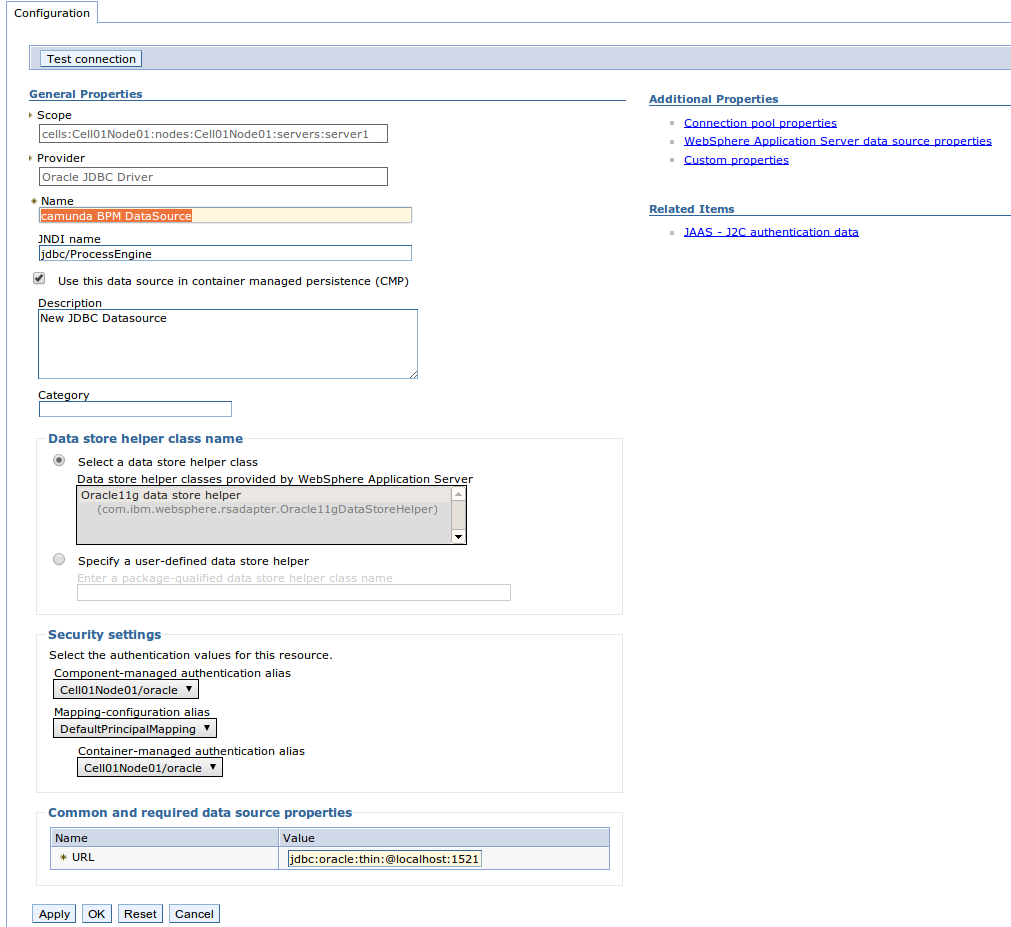
Note that you may configure multiple datasources used by different process engine instances. See the User Guide for details.
Configure a WorkManager
This section explains how you can use the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console to configure a work manager to be used by the Camunda Platform jobexecutor. It is recommended to check the manual of the application server for additional details.
Go to Resources / Asynchronous Bean / Work Managers (Websphere 8) or Resources / Concurrency / Work Managers (Websphere 9). Select the appropriate scope, for example: Cell=<some_id>.
Create a new work manager in the scope using the Button New….
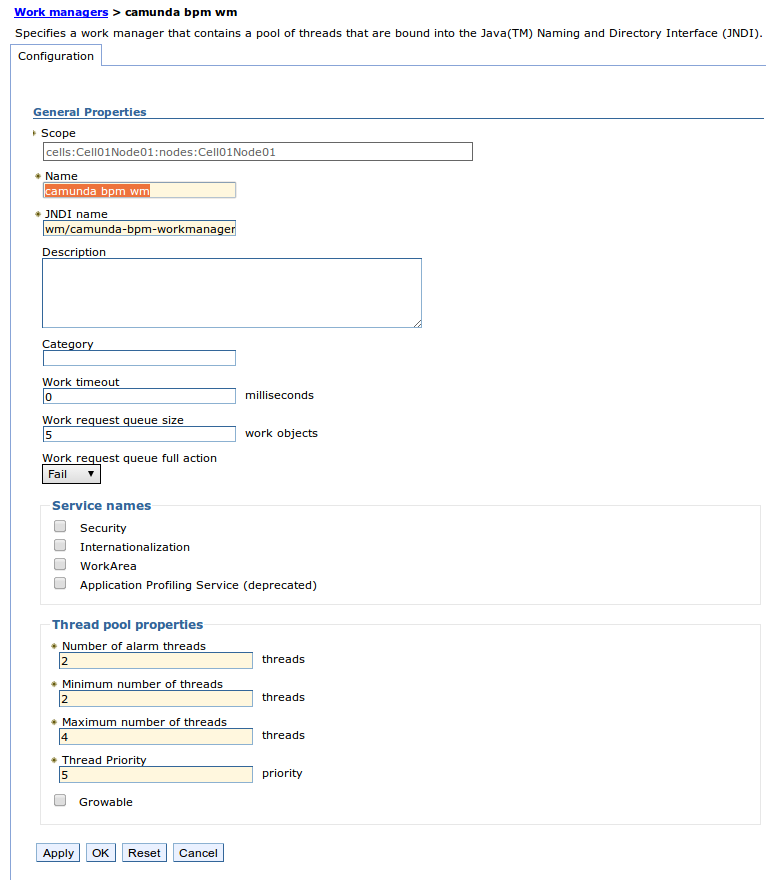
Configure the new Work Manager. The following is a selection of sensible default values:
General Properties
| Property | Default Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Name | camunda-platform-jobexecutor-WM | The name of the Work Manager. |
| JNDI name |
wm/camunda-bpm-workmanager |
Default JNDI name for WorkManager. This setting value is mandatory and must not be changed. |
| Description | "The work manager used by the Camunda platform job executor" | Describes the work manager. Any value can be used. |
| Work Request Queue Size | 5 | Specifies the size of the work request queue. The work request queue is a buffer that holds scheduled work objects and may be a value of 1 or greater. The thread pool pulls work from this queue. If you do not specify a value or the value is 0, the queue size is managed automatically. Large values can consume significant system resources. |
| Work request queue full action | Fail | Specifies the action that is taken when the thread pool is exhausted, and the work request queue is full. This action starts when you submit non-daemon work to the work manager. The default value is block but should be changed to "Fail". |
Thread Pool Properties
| Property | Default Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Number of alarm threads | 2 | Specifies the desired maximum number of threads that are used for alarms. The default value is 2. |
| Minimum number of threads | 2 | Specifies the minimum number of threads that are available in this work manager. Should not be below "2" since one thread is blocked by the job acquisition. If you configure multiple job acquisitions, the Minimal Size should not be below Nr. of Acquisitions + 1. |
| Maximum number of threads | 4 | Specifies the maximum number of threads that are available in this work manager used by the jobexecutor. Should be greater than "Minimum Size". |
| Thread Priority | 5 | Specifies the priority of the threads that are available in this work manager. |
| Growable | False | Specifies whether the number of threads in this work manager can be increased automatically when the maximum number of threads is reached.The default value is true, but should be changed to "False" |
The following screenshot shows an example configuration of the work manager and its thread pool properties.
Required Components
The following steps are required to deploy the Camunda Platform.
Camunda Shared Libraries
The shared libraries include the Camunda engine and some utility JARs. The shared libraries must be visible to both the Camunda Platform as well as all process applications.
The shared libraries can be found in the lib folder of the distribution:
camunda-ee-ibm-was-$PLATFORM_VERSION.zip
|-- modules/
|-- lib/ <-- The shared libs
|-- camunda-engine-$PLATFORM_VERSION.jar
|-- java-uuid-generator-XX.jar
|-- mybatis-XX.jar
|-- joda-time-XX.jar
|-- ...
|-- camunda-ibm-websphere-ear-$PLATFORM_VERSION.ear
Copy the shared libraries into a folder, where it can be referenced from your IBM WebSphere Server installation.
Next, go to Environment / Shared libraries, choose the correct scope in which your EAR and applications will run and define a new shared library.
Name it Camunda. This name is mandatory, except when you modify the deployment.xml which is located inside the Camunda Platform EAR accordingly.
Enter as classpath the path where you have copied the Camunda shared libraries, e.g., /opt/IBM/WebSphere/AppServer/profiles/AppSrv01/camunda-shared-libs. Enable
the Use an isolated class loader for this shared library checkbox. Restart the IBM WebSphere Server after this operation.
Camunda Platform EAR
The Camunda Platform distribution for IBM WebSphere Application Server includes one module in the modules folder:
camunda-ee-ibm-was-$PLATFORM_VERSION.zip
|-- modules/
|-- camunda-ibm-websphere-ear-$PLATFORM_VERSION.ear
The camunda-ibm-websphere-ear is a Java EE application enterprise archive (EAR) providing the Camunda Platform services. It contains an embedded rar module. This camunda-ibm-websphere-rar module is a JCA Resource Adapter providing the jobexecutor service to the Camunda Platform.
The EAR must be installed to your IBM WebSphere Application Server:
- Navigate to the Enterprise Applications page using the navigation path Applications / Application Types / WebSphere enterprise applications.
- Click the “Install” Button.
- Select the
camunda-ibm-websphere-ear-$PLATFORM_VERSION.earfile from the modules folder of the Camunda Platform for IBM WebSphere Application Server distribution. Click Next. - Select the “Fast Path” install option.
- In Step 1, enter an application-name, eg. “camunda-bpm-platform”, customize other settings and click “Next”.
- Continue through Steps 2-4, customize to your liking and finish the installation in Step 4 by clicking “Finish”.
- Save the configuration.
- (optional) Configure location of the bpm-platform.xml file
- Start the camunda-bpm-platform application. If this initially fails, try to restart the server. Also make sure the EAR does correctly reference the previously created ‘Camunda’ shared library. If it doesn’t, make sure you have correctly created the shared library as ‘Camunda’ or assign the ‘Camunda’ shared library manually after the EAR installation.
Optional Components
This section describes how to install optional components. None of these are required to work with the core platform.
Cockpit, Tasklist and Admin
The web application archive that contains Camunda Cockpit and Camunda Tasklist resides under $WAS_DISTRIBUTION/webapps/camunda-webapp-ee-was-$PLATFORM_VERSION.war in the IBM WebSphere Application Server distribution archive.
In this section we explain how to install the WAR file using the IBM WebSphere enterprise application wizard provided by the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console:
- Open the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console.
- Navigate to the Applications / Application Types / WebSphere enterprise applications page.
- Click the Install Button
- The first page of the wizard opens. Using the file browser, select the
camunda-webapp-ee-was-$PLATFORM_VERSION.warfile from the distribution and upload it. - Continue to the next page.
- Select the “Fast Path” on the next page.
- Step 1. Usually no changes are required.
- Step 2. Usually no changes are required.
- Step 3. Usually no changes are required.
- Step 4. Define a context root for the applications. We propose to use /camunda
- Step 5. Usually no changes are required.
After completing the wizard, the applications should be successfully installed on the application server. Don’t forget to save your changes to the master configuration.
The final step is to reference the shared libraries. To do so, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Applications / Application Types / WebSphere enterprise applications page.
- Click on the name of the application (e.g., camunda-webapp-ee-was-7_2_0-ee_war).
- Click on Shared library references.
- Click on the checkbox next to the application name and click on the Reference shared libraries button.
- Select the shared library Camunda.
- Confirm selection by clicking on OK.
In some situations, you have to start the web application manually from the Applications / Application Types / WebSphere enterprise applications page.
You can check if everything went well by accessing Cockpit and Tasklist via /camunda/app/cockpit and /camunda/app/tasklist or under the context path you configured.
REST API
The Camunda REST API WAR file resides under $WAS_DISTRIBUTION/webapps/camunda-engine-rest-$PLATFORM_VERSION-was.war in the IBM WebSphere Application Server distribution archive.
In this section we explain how to install the WAR file using the IBM WebSphere enterprise application wizard provided within the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console:
- Open the WebSphere Integrated Solutions Console.
- Navigate to the Applications / Application Types / WebSphere enterprise applications page.
- Click the Install Button
- The first page of the wizard opens. Using the file browser, select the
camunda-engine-rest-$PLATFORM_VERSION-was.warfile from the distribution and upload it. - Continue to the next page.
- Select the “Fast Path” on the next page.
- Step 1. Usually no changes are required.
- Step 2. Usually no changes are required.
- Step 3. Usually no changes are required.
- Step 4. Define a context root for the REST API. We propose to use /engine-rest
- Step 5. Usually no changes are required.
After completing the wizard, REST API should be successfully installed on the application server. Don’t forget to save your changes to the master configuration.
The final step is to reference the shared libraries. To do so, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Applications / Application Types / WebSphere enterprise applications page.
- Click on the name of the application (e.g., camunda-engine-rest-7_2_0-ee-was_war).
- Click on Shared library references.
- Click on the checkbox next to the application name and click on the Reference shared libraries button.
- Select the shared library Camunda.
- Confirm selection by clicking on OK.
In some situations, you have to start the web application manually from the Applications / Application Types / WebSphere enterprise applications page.
Camunda Connect Plugin
Add the following artifacts (if not existing) from the folder $WAS_DISTRIBUTION/modules/lib to the Camunda shared library folder:
camunda-commons-utils-$COMMONS_VERSION.jar
In order to activate Camunda Connect functionality for a process engine, a process engine plugin has to be registered in the Camunda Platform configuration as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bpm-platform ... >
<process-engine name="default">
...
<plugins>
... existing plugins ...
<plugin>
<class>org.camunda.connect.plugin.impl.ConnectProcessEnginePlugin</class>
</plugin>
</plugins>
...
</process-engine>
</bpm-platform>
Note that this requires a custom bpm-platform.xml file.
Camunda Spin
Add the following artifacts (if not existing) from the folder $WAS_DISTRIBUTION/modules/lib/ to the Camunda shared library folder:
camunda-spin-core-$SPIN_VERSION.jarcamunda-commons-utils-$COMMONS_VERSION.jar
In order to activate Camunda Spin functionality for a process engine, a process engine plugin has to be registered in the Camunda Platform configuration as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bpm-platform ...>
...
<process-engine name="default">
...
<plugins>
... existing plugins ...
<plugin>
<class>org.camunda.spin.plugin.impl.SpinProcessEnginePlugin</class>
</plugin>
</plugins>
...
</process-engine>
...
</bpm-platform>
Note that this requires a custom bpm-platform.xml file.
Groovy Scripting
Add the following artifacts (if not existing) from the folder $WAS_DISTRIBUTION/modules/lib/ to the Camunda shared library folder:
groovy-all-$GROOVY_VERSION.jar
GraalVM JavaScript Integration
Add the following artifacts (if not existing) from the folder $WAS_DISTRIBUTION/modules/lib/ to the Camunda shared library folder:
graal-sdk-21.1.0.jaricu4j-68.2.jarjs-21.1.0.jarjs-scriptengine-21.1.0.jarregex-21.1.0.jartruffle-api-21.1.0.jar
Process Applications
After installing a Process Application (PA) in your IBM WebSphere Application Server, which does not include the Camunda Platform dependencies, you must assign the previously created “Camunda” shared library with the Process Application deployment. This should only be necessary when you use the “shared” engine deployment approach and not the “embedded” process engine one (aka self-contained Process Application).
Troubleshooting
Define IBM WebSphere Resources in the right scope
When installing the Camunda Platform application, you may see error messages indicating that you are referencing resources from the wrong scope. Make sure you define the resources in the right scope so all components are visible to each other. Make sure you understand the IBM WebSphere management concepts “Cell”, “Node” and “Server”.